Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis, Bursitis, and Impingement
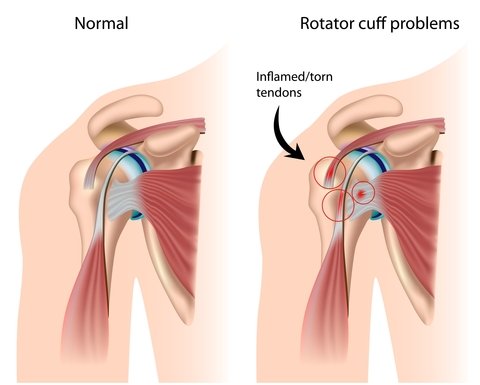
A group of four muscles around the shoulder joint make up the rotator cuff. These include the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The tendons which attach these four muscles to the humerus are known as the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff has several important jobs, including stabilizing the shoulder, elevating and rotating the arm, and ensuring the head of the humerus stays securely in the shoulder joint. Rotator cuff pain is very common.
Rotator cuff impingement, bursitis, and tendonitis are three different diagnoses but have very similar symptoms and treatment. These are all characterized by inflammation and pain primarily coming from the area of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. Symptoms commonly include pain over the outside of the shoulder when reaching and lifting over the head.

Treatments for Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
-
Avoid activities that re-create the sharp pain as best as possible. Limit repetitive reaching or lifting.
-
Ice packs should be applied to the shoulder to help with pain.
-
Physical therapy is important to strengthen and rebalance the muscles of your shoulder. PT helps decrease pain and inflammation in the shoulder.
-
NSAIDS such as ibuprofen or naproxen help with swelling and pain.
-
Ultrasound-guided injections of corticosteroids around the rotator cuff can provide improvement in pain and inflammation.
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is made by concentrating the growth factors in your blood to help your body heal. PRP is injected under ultrasound guidance in and around the injured tendon. Learn more here.